In times when external appearance is as important as internal health of an individual, any growth or eruption seen on a person’s external body causes a lot of speculation as to what it Is, how it has come up and most importantly how to get rid of it. If such a thing appears especially in children it is important for the parents to make sure that it is cured permanently without any side effects. One of such commonly seen eruptions in children and young adults is Molluscum Contagiosum. Although Molluscum Contagiosum is a common skin rash in kids, many parents have never heard of it, so are often caught unaware in such a situation.
What is Molluscum Contagiosum?
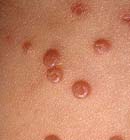
Molluscum Contagiosum is a viral infection that causes a mild skin rash. The rash looks like one or more small growths or wart-like bumps (called Mollusca) that are usually pink, white, or skin-colored. The bumps are usually soft and smooth and may have an indented center.
- Infection is most common among kids between 1 and 12 years old.
- Teens and adults
- Some athletes, such as wrestlers, swimmers, and gymnasts
- People whose immune systems have been weakened by HIV, cancer treatment, or long-term steroid use.
Causes
As you might guess by its name, this skin disorder is contagious, and can easily be passed from one person to another.
- Molluscum Contagiosum is caused by the Molluscum Contagiosum Virus (MCV), a member of the Poxvirus family. This virus thrives in warm, humid climates and in areas where people live in very close, cramped, and unhealthy environments.
- Infection with MCV occurs when the virus enters a small break in the skin’s surface. Many people who come in contact with the virus have immunity against it, and do not develop any growths. For those not resistant to it, growths usually appear 2 to 8 weeks after infection.
- Kids can get Molluscum Contagiosum in different ways. It spreads easily, and most commonly, through direct skin-to-skin contact, but kids also can get it by touching objects that have the virus on them, such as toys, clothing, towels, and bedding.
- Once someone has Molluscum Contagiosum, it spreads from one part of the body to another by scratching or rubbing the bumps and then touching another part of the body.
- Molluscum Contagiosum can also be spread between sexual partners.
Signs and Symptoms
- Being a skin infection, the only real sign or symptom of Molluscum Contagiosum is the appearance of small round pink, white, or skin-colored Mollusca on the skin. These bumps are filled with a white, waxy pus core that contains the virus, and might have a shiny or “pearly” look.
- Each Molluscum starts out as a very small spot about the size of a pinhead and grows over several weeks into a larger bump that might become as large as a pea or pencil eraser.
- The Mollusca can appear alone as a single bump or in groups, clusters, or rows. They can show up almost anywhere on the skin, but in kids are most commonly found on the chest, stomach, arms (including the armpits), legs, and face.
- In sexually active teens and adults, the bumps are usually located in the genital area or the inner thighs. Rarely, the bumps can occur around the eyes and in or around the mouth.
- Most people develop between 1to 20 Molluscs. They’re usually painless, but can become itchy, red, swollen, sore, and infected, especially if scratched.
- Molluscum Contagiosum generally causes no long-term problems, and the growth usually leaves no marks. However infected lesions might scar the skin in cases where there is a development of secondary infection.
- People with weakened immune systems can sometimes get a more serious form of Molluscum Contagiosum. They typically have more Mollusca, especially on the face. The growths are larger, look different, and take longer time to respond to treatment.
Homeopathic Management
- Homeopathy treats not only the superficial lesions but the patient as a whole is taken into consideration and the disease is removed from the root. All different types of lesions indicate different medicines pertaining to the type of lesion, associated complaints and general health and tendencies of the patient.
- Remedies like Causticum are indicated when along with eruptions the children look very pale, weak and debilitated.
- Bromium covers eruptions on arms and face in children with a tendency to enlarge glands.
- Thuja, Kali Iod and Natrum Mur cover the miasmatic background and are useful as intercurrent medicines.
- Selection of homeopathic treatment also depends upon the symptoms the patient is experiencing along with eruptions. No surgical intervention like freezing the eruptions needs to be done and the patient can be completely cured of the condition by a homeopath, who has the sensitivity to decide the medicine and its dosage to be given to get effective results.
Preventing the Spread of Molluscum Contagiosum
Since molluscum contagiosum is contagious and can spread to other parts of the body, someone who’s infected should follow these precautions:
- Do not touch, scratch, or rub the growths.
- Wash hands often with soap and water.
- Keep areas with growths clean.
- Try to cover each growth with clothing or a watertight bandage, especially before participating in activities in which equipment is shared or skin contact can occur, like swimming and wrestling.
- Change each bandage daily or when it becomes dirty.
- Do not shave over areas that have bumps.
- Do not share towels, clothing, and other personal items.