Diaper Rash
- Diaper rash or diaper dermatitis is a form of irritant contact dermatitis. Increase in the moisture content in and around the perianal region leads to overhydration of the skin leading further to friction and breaking of the skin.
- It can normally involve any site in and around the perianal region, although the folds of skin are usually spared. They appear as red, itchy lesions that can sometimes bleed and even break. Secondary infection with bacteria or yeast can occur commonly in severe cases.
- One form of rash in the nappy area may be caused by a fungus called candida albicans. It is usually mild but has a tendency to recur. One of the causes for its recurrence is that most of these infants carry candida in their intestines and the warm, moist environment of the diaper area predisposes to cause infection.
- Causes of diaper rash include soiled diapers left for a prolonged period of time, prolonged contact with urine and feces, certain types of soaps and detergents.
- Introduction of new foods can affect a change in the feces content, predisposing to a diaper rash. Also diarrhea can worsen the condition.
Eczema / Atopic Dermatitis
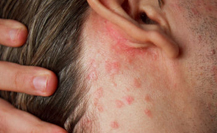
- Eczema is a form of dermatitis where there is inflammation of the outer layer of the skin, it is characterized by the skin becoming dry, red, irritated and itchy.
- Eczema has been classified into various types and the commonest one is atopic eczema or also medically termed as atopic dermatitis.
- Other types of eczema include: contact dermatitis, xerotic eczema i.e winter itch where the condition worsens in winter, seborrheic dermatitis also called as cradle cap in infants and is closely related to dandruff.
- Eczema is more the description of a symptom rather than a disease and can be manifested due to many internal and external factors acting singly or in combination with each other.
- In case of irritant contact dermatitis, after exposure to a mild irritant such as a detergent, the child may develop a rash.
- Allergic contact dermatitis develops when an allergen (substance to which a person is allergic) touches the skin. Common allergens include poison ivy and nickel.
- In other types of eczema, a variety of genetic and environmental factors play a role.<br>
- Eczema can occur acutely or can be chronic with repeated acute flare ups.
- Its presentation is characterized by hot, red, itchy skin with redness and swelling, papules, vesicles or large blisters, exudation and crusting and scaling.
- Chronic eczema is less vesicular, more scaly but also pigmented and thickened and more likely to develop painful blisters.
- Some babies are born with eczema; others develop it soon after birth. In such cases one can point out an inherited tendency or predisposition and there may be a family history of asthma, allergies or skin problems.
The Homeopathic Approach
- The Homeopathic approach for Eczema is to treat the child as a whole rather than treating only the disease. Eczema is simply an external presentation of an internal disorder due to lowered vitality and immunity. When the whole person is treated, the power of the immune system is enhanced thereby causing the disease to disappear.
- A constitutional remedy (specific to the individual) is selected by assessing the physical, mental and emotional states, family history, and the past health history of the person. The type of eczema, location, aggravating and relieving factors will be taken into consideration, besides many other factors in choosing the remedy.
Urticaria/Rashes
- Urticaria is an itchy rash associated with localized swelling (wheals) on the skin that usually lasts for a few hours to days before fading away. It is also known as hives and is a common skin condition.
- Urticaria is an indication that the whole body is experiencing a Hypersensitivity reaction.
- The wheals can be a few millimeters or several centimeters in diameter, colored white or red, usually itchy, swollen and can appear in groups.
- Each wheal may last a few minutes or several hours, and may change shape and appear round, or form rings, a map-like pattern, or giant patches. Hives may or may not be accompanied by swelling of eyelids, lips, hands or other parts of the body. This swelling is known as “Angioedema”.
- Acute urticaria resolves in a few hours to days. Sometimes urticaria may occur daily and last more than two months.
- Due to a reaction in the body the cells in the skin called mast cells release histamine, a chemical that causes tiny blood vessels (capillaries) to leak fluid. When this leaking fluid accumulates in the skin, it appears as small swellings that we classify as Urticaria or Hives.
Causes & Symptoms
- In the majority of cases of chronic urticaria, the cause is not known. Though it’s not very easy to determine the exact cause of such a reaction in a child but we can surely find out if there is any genetic predisposition, environmental allergens, food allergens, drug allergens or any systemic illness which leads to altered immunity and a reaction in the body in the form of urticaria.
- The common triggers in everyday life that can cause histamine release and cause urticaria are nuts, chocolate, fish, tomatoes, eggs, fresh berries, and milk. Fresh foods can cause a reaction more than cooked foods. Food additives and preservatives may also cause hives.
- Firmly rubbing or scratching the skin can cause Urticaria.
- Cold-induced Urticaria appears when a child is exposed to sudden low temperatures ¬ for example, after a plunge into a swimming pool or when an ice cube is placed against the skin.
- Other commonly seen causative factors are Hot showers, excessive sweating, and sun exposure.
- Certain medications like antibiotics, Flu vaccine, tetanus toxoid vaccine etc can also cause urticaria.
- Many infections like common cold, strep throat, infectious mononucleosis, Worm infestation can also lead to such a reaction in the body.
- Certain Insect stings or pressure clothing like bands and socks can also cause urticaria.
The Homeopathic Approach
- Urticaria is nothing but an external expression of internal, immunological disturbance; hence the treatment of urticaria should also be based on the inner level consideration.
- Our treatment is not aimed at only relieving the outer expression of the complaints but to treat the problem at a deeper level.
- The homeopathic approach not only treats urticaria but also eliminates the tendency to the hypersensitivity by treating the underlying cause.
Chicken Pox
- Chickenpox is one of the commonest skin infections of childhood. It is characterized by the development of elevated boil-like vesicles that are filled with fluid, itchy lesions all over the body.
- Chickenpox spreads through contact with the fluid of skin lesions, either by airborne spread or through direct contact. The patient can transmit the infection 2 days before the appearance of rash and until the vesicles get crusted i.e. upto 3-7 days after the development of the rash. By itself, the infection dies down on its own, usually with no long term complications.
- The symptoms are seen in the form of fever, malaise, loss of appetite, headache start followed by appearance of the rash. The lesions usually appear first on the scalp, face or trunk. They spread to the rest of the body and start crusting in 24-48 hours.
- By the 14th day of infection, blistering stops and most of the scabs fall off. A few weeks after this, the scars disappear. Rarely does chickenpox leave lasting scars.
- As a complication the vesicles may get infected with bacteria and sometimes when the infection is very high there is a risk of complications, including pneumonia, skin infections, blood infections, or brain infection. If fever persists or there are signs of infections such as warmth, redness, or swelling of the skin, immediate medical attention is required. The internal organs of the body such as the liver, lungs may also get affected.