A flawless complexion is every woman’s dream & desire irrespective of their age. Any change in appearance of her skin during any period of life becomes a major cause of anxiety to her. Skin pigmentation conditions can be a problem for all women with brown skin – especially people of Asian, African, Latin or Native American backgrounds. While the natural pigmentation in brown skin provides many advantages – sun protection and slowed signs of aging – it is also more highly susceptible to skin discolorations.
Sometimes the cells that contain the melanin pigment are damaged or over stimulated. When this happens, the affected cells may begin to produce too much or too little melanin. Too much melanin causes darker spots or patches, while too little causes lighter spots or patches. These lighter or darker spots appear on the surface of the skin, and can be unsightly.
There are a number of pigmentation disorders that affect the skin. These include:
It is a skin pigmentation disorder that results from functional problems with cells that produce and contain the melanin pigment. This dysfunction results in the appearance of irregular brown or grayish-brown marks on facial skin. In melasma, the dark spots and patches usually affect the nose, cheeks, forehead, upper lip and chin in three different patterns.
- Melasma can occur in all skin types and in people of all racial and ethnic groups, but is most common in women with brown skin who are between the ages of 21 and 40.
- It is sometimes referred to as the “mask of pregnancy” because it occurs commonly during pregnancy and in women who take oral contraceptive pills.
- People living in areas of intense and prolonged sunlight (Asia, Africa, Latin America and the Caribbean) are more susceptible to developing melasma.
When melasma affects women due to pregnancy, it may resolve within a few months after delivery and treatment may not be necessary. There are, however, many cases in which the disorder persists indefinitely. Even when treated successfully, melasma often recurs, especially when the skin is exposed to the sunlight.
For all individuals with melasma, it’s imperative to wear a broad-spectrum (UVA plus UVB) sunscreen daily.
- Avoid the sun when possible, and wear protective eyewear, caps, hats and clothing.
- When melasma develops in response to hormone treatment, either oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy, patients should consult with their physicians to discuss discontinuation of the hormones.
Post Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
A condition that is especially prevalent among women of African and Latino descent, who have a high incidence of hypertension, diabetes and heart disease and consequently take medications for those medical problems that can cause various types of allergic reactions that frequently lead to hyper-pigmentation and dark spots or patches.
Women with brown skin, particularly those of African and Latino descent, have a high incidence of hypertension, diabetes and heart disease and consequently take medications for those medical problems.
These medications can cause various types of allergic reactions that frequently lead to hyperpigmentation and dark spots or patches on the skin. There are four primary types of medication reactions that can lead to hyperpigmentation:
- Fixed drug eruptions
- Photosensitivity reactions
- Drug-induced hyperpigmentation
- Drug eruptions with secondary post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- A fixed drug eruption is a round, dark patch or eruption that results from a reaction to a drug (usually a prescription medication). This type of reaction leaves a grey-blue, round patch on the skin. The round patch is usually fixed to one spot and will appear in this same location within 24 hours of each dose taken.
- Photosensitivity reactions occur as a result of a direct interaction between the sun and a medication that you are taking. In the case of a photosensitive reaction, brown or blue-grey patches will develop in areas of the skin exposed to the sun, including the face, tops of the ears, V of the neck, and outside of the arms.
- Drug-induced hyperpigmentation is hyperpigmentation (dark patches) caused by a reaction between a component of the medication and your skin. The pigmentation often occurs on the face, especially around the mouth. Other parts of the body may be affected as well.
- Secondary post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation occurs when dark marks remain in an area after a primary allergic rash has been resolved.
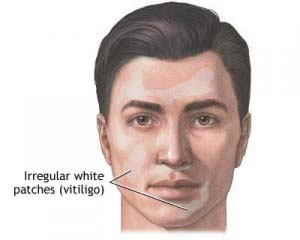
Vitiligo
It is a skin disorder in which the cells that make melanin pigment (melanocytes) are destroyed. The destruction results in the loss of pigment and the appearance of irregular white patches on the skin.
Vitiligo is a skin disorder in which the cells that make melanin pigment (melanocytes) are destroyed. The destruction results in the appearance of white patches on the skin. Vitiligo can occur at any age, but usually occurs before the age of 20 in about 50% of patients.
There are five main types of vitiligo, which are based upon the location of the white patches and the pattern of involvement: focal, generalized, acrofacial, segmental and universal.
- Focal Vitiligo minimal involvement with only one or a very few white patches scattered on the skin
- Generalized Vitiligo the most common type with symmetrical patches on any location on the skin including the trunk and/or extremities
- Acrofacial Vitiligo white patches limited to the fingers and around the mouth and eyes
- Segmental Vitiligo white patches on one side of the body and in a linear or line-like distribution (dermatome)
- Universal vitiligo Widespread patches involving almost the entire body
The cause of vitiligo is not well understood. It is believed to be an autoimmune disorder which means that certain blood cells in your body, lymphocytes, turn against and attack the melanocytes. Another theory is that vitiligo is caused by an interaction between the body’s nerve cells and melanocytes.
Vitiligo may be associated with other immune disorders. They include Addison disease (an adrenal gland disorder), alopecia areata, diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, parathyroid disease, melanoma, chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis (yeast infection), pernicious anemia, and uveitis (eye disorder).
Homeopathy for Skin Pigmentation
Homeopathy believes that skin disorders are a reflection of the inside & need to be treated from within. A well indicated & well prescribed homeopathic medicine not only takes care of hyperpigmentation but also treats the person as a whole & there is improvement of general health as well.
We have medications which treat hormonal imbalance & thereby tackling excessive production of melanin. The texture of skin improves & occurrences of new patches ultimately stop.
Homeopathic remedy Sepia is a boon to the ladies for helping them in pigmentation of various kinds.
We have highly indicated miasmatic medicines which reduce the tendency of the body to produce excessive melanin & also remove the tendency of hypersensitivity to sunlight.
Medicines like Iodium & Caulophyllum are like homeopathic beauty medicines which help in attaining a flawless skin.
Skin pigmentation arising due to side effects of other therapies or drugs can also be tackled with homeopathy & it helps to remove the underlying problem & bring about a complete cure.
Sepia (homeopathic medicine) is of utmost importance in treating discoloration occurring after pregnancy. In fact, it is apt for what one would call a post-pregnancy syndrome ? a brownish saddle-like appearance spreading across the nose, backache, easily fatigued constitution, heightened mental sensitivity and irritability. Other medicines that are important in treatment are arsenic album and conium maculatum.
Sun-damaged skin or sunspots, medically called lentigos, and commonly referred to as liver spots, are a product of sun exposure. This exposure is cumulative and not directly related to sunburn on a specific day.
Homeopathy does not advocate the use of creams and ointments in skin disorders. It believes that skin disorders are a reflection of inside and need to be treated from within. Another strong opinion that homeopaths propagate is that any external application can lead to the suppression of the disease and result in a more serious systemic disorder. A well-prescribed homeopathic medicine not only takes care of hyperpigmentation but also treats as a whole and improves general health as well.
Homoeopathic medicines treat the hormonal imbalance and thus control the excessive production of melanin. The texture of the skin also improves. The occurrences of new patches reduce and ultimately stop. The skin slowly reverts to its normal condition without leaving any blemishes.
General precautions for people suffering from hyperpigmentation: stay out of the sun so that these areas don’t darken even more. If you can’t avoid the sun, wear hats, cover up. Along with it, eat a well-balanced diet, avoid cosmetics, avoid direct exposure of skin to sunlight and please do not self-medicate.