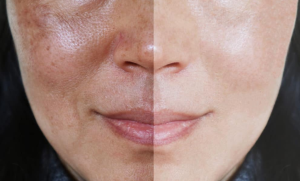
What is the melasma
Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by the development of brown or grayish-brown patches on the skin, primarily on the face. It occurs due to the overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for the colour of our skin, hair, and eyes. Melasma is more prevalent in individuals with darker skin tones and is more common in women than men, especially during their reproductive years. While it is not a harmful medical condition, it can cause cosmetic concerns and affect a person’s self-esteem.
Who can be affected by it?
- The condition is much more common in women than men, though men can get it too.
- According to survey 90 percent of people who develop melasma are women.
- Melasma is a very common skin disorder, especially among pregnant women. 15% to 50% of pregnant women get it.
- Between 1.5% and 33% of the population may get melasma and it happens more often during a woman’s reproductive years, and rarely happens during puberty.
- It usually starts between 20 and 40 years of age.
WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF MELASMA :-
- Epidermal: Epidermal melasma has a dark brown colour, a well-defined border, appears obvious under black light and sometimes responds well to treatment.
- Dermal: Dermal melasma has a light brown or bluish colour, a blurry border, appears no differently under black light and doesn’t respond well to treatment.
- Mixed melasma: Mixed melasma, which is the most common of the three, has both bluish and brown patches, shows a mixed pattern under black light and shows some response to treatment
What are the causes of Melasma
Etiologic factors include genetic influences, ultraviolet (UV) radiation, pregnancy, hormonal therapies, cosmetics, phototoxic drugs, and antiseizure medications.
Melasma stimulates melanocytes by the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone, producing more melanin pigments when the skin is exposed to the sun.
Genetic
Genetic predisposition may be a major factor in the development of melasma.
- Melasma is more common in females than in males.
- Persons with light-brown skin types from regions of the world with high sun exposure are more prone to the development of melasma.
- Approximately 50% report a positive family history of the condition. Identical twins have been reported to develop melasma.
Sunlight Exposure
UV radiation can cause lipids peroxidation in cellular membranes, resulting in free radicals which could stimulate melanocytes to produce excess melanin.
- Sunscreens that block UV-B radiation (290-320 nm) do not block the longer wavelengths of UV-A and visible radiation (320-700 nm) which also stimulate melanocytes to produce melanin.
LED Screens:
Melasma may be caused by the LED lights from your television, laptop, cell phone and tablet.
Hormonal Influences
Hormones may play a role in developing melasma in some individuals.
- The mask of pregnancy is known to occur in obstetric patients. The exact mechanism is unknown. Estrogen, progesterone, and melanocyte-stimulating hormone levels are normally increased during the third trimester of pregnancy and may be a factor.
- Patients with melasma who are nulliparous have no increased levels of estrogen or MSH but show elevated levels of estrogen receptors within the lesions. In addition, melasma with estrogen- and progesterone-containing oral contraceptive pills and diethylstilboestrol treatment for prostate cancer have been observed.
- A woman who is postmenopausal and given progesterone may develop melasma, while those who are given estrogen alone do not; this implicates progesterone as playing a primary role in the development of melasma.
Thyroid Disease
There is a four-fold increase in thyroid disease in melasma patients.
- There is an association between the development of melasma and the presence of melanocytic nevi and lentiginous nevi.
- This would indicate a relationship between the development of melasma and the presence of pigmentation.
What are the symptoms of Melasma
- Melasma causes patches of discoloration. The patches are darker than your usual skin color.
It typically occurs on the face and is symmetrical, with matching marks on both sides of the face.
- Other areas of your body that are often exposed to sun can also develop melasma.
- Brownish coloured patches usually appear on the:
- cheeks
- forehead
- bridge of the nose
- chin
Diagnosis
- A visual exam of the affected area is often enough to diagnose melasma. To rule out specific causes, your healthcare professional might also perform some tests.
- One testing technique is a Wood’s lamp examination. This is a special kind of light that’s held up to your skin. It allows your healthcare professional to check for bacterial and fungal infections and determine how many layers of skin the melasma affects.
- To check for any serious skin conditions, they might also perform a biopsy. This involves removing a small piece of the affected skin for testing.
How to prevent of Melasma
While not all cases of melasma will clear up with treatment, there are things you can do to make sure the condition doesn’t get worse and to minimize the appearance of the discoloration. These include:
- Using makeup to cover areas of discoloration
- Taking prescribed medication
- Wearing sunscreen every day with SPF 30
Wearing protective clothing is especially important if one will be in the sun for an extended period of time.
Triggers:
Certain factors can exacerbate melasma or trigger its onset, including excessive sun exposure without proper protection (sunscreen and protective clothing), hormonal fluctuations, and the use of certain medications that may increase sensitivity to UV rays.
HOW HOMEOPATHY HELPS IN MELASMA
Melasma is a manifestation of an underlying imbalance or disturbance in the body’s vital force (life force). Homeopaths aim to identify the unique symptoms and characteristics of the individual with melasma to prescribe a highly diluted remedy that matches the person’s overall symptom picture.
During a homeopathic consultation for melasma, a practitioner will gather detailed information about the person’s physical symptoms, emotional state, lifestyle, and overall health. They will consider the pattern of pigmentation, any triggers or aggravating factors, and any other associated symptoms to choose a suitable homeopathic remedy.
Homoeopathy has safe and effective remedies for treating the melasma it helps by restoring and even tone to skin and controlling further progression of pigmentation
FEW HOMEOPATHIC MEDICINES WHICH HELP IN MELASMA
1. Sepia officinalis:
Sepia is one the excellent remedies for melasma. There is yellowish- brownish spots on face, especially cheeks, forehead and cheeks and nose.
A yellow saddle across the upper part of cheeks and nose. There is dark circle under the eyes. Facial discoloration during pregnancy, after childbirth and menopause .Sepia is suited to persons having dark hair, and rigid fibre.
2. Berberis Aquifolium:
For Treating Facial Pigmentation from Eruptions Berberis Aquifolium is a highly effective and reliable remedy for treating pigmentation spots and scars on the face left behind by any kind of eruption.
The skin may feel waxy, the cheeks may feel how, skin becomes dry, rough, scaly and pimply and it clears the skin.
4. Cadmium Sulphuratum:
For facial pigmentation that gets worse with exposure to the sun, Cadmium Sulphuratum is the best prescription. The pigmentation varies from yellowish to brownish in colour
Pigmented spots are present over the entire face, but most prominently on the nose and cheeks. Another guiding symptom for use of Cadmium Sulphuratum is that pigmentation gets worse in the wind. The face may feel itchy. Pigmentation that Worsens in Sun.
5. Pulsatilla Nigricans:
It is a most effective medicine for facial pigmentation in women with menstrual irregularities. The irregularities include delayed periods, scanty menses and suppressed menses. They show up as pigmented spots and freckles on the face. Pulsatilla is also helpful for acne resulting from menstrual irregularities.
6. Psorinum:
For facial pigmentation attended with greasy, oily, waxy skin, Psorinum is the medicine to go to. Facial skin looks dull, pale and sick. The face is covered in pigmented spots that may be attended with itching. Acne – papular or pustular – may be present on the face.
7. Sulphur:
Sulphur is a highly reliable medicine for facial pigmentation with dry skin. The skin looks unhealthy and dirty. The person complains of itching and burning sensation on the face. Itching gets worse in the heat. Sulphur is also a good choice of medicine to treat facial pigmentation that has been subjected to ointments and external topical applications in the past.
There are many medicines in homeopathy if given in exact dose and potency after matching the totality of symptoms of the patient with that of the medicine, ease the suffering of the patient, so one should seek an expert’s opinion before starting the homeopathic treatment for Melasma.
Why Cosmic Homeo Healing Centre?
Cosmic Homeo Healing Centre is run by second generation Homeopath Dr. Mahavrat Patel having vast clinical records of more than 75 years and clinical experience of nearly 50 years in the treatment of various cases of Melasma. Under the able guidance of Dr. Mahavrat Patel, our team of experts has been successfully treating thousands of cases of Melasma for many years.